CAD Designer's
Quick Reference
Fast lookup tool for component selection in mechanical design projects
Find Components Quickly
Search across all component categories to find exactly what you need for your project
Component Categories
Comprehensive reference for the most commonly used mechanical components in CAD design projects
Electric Motors
DC, AC, stepper, servo, and linear motors for all applications
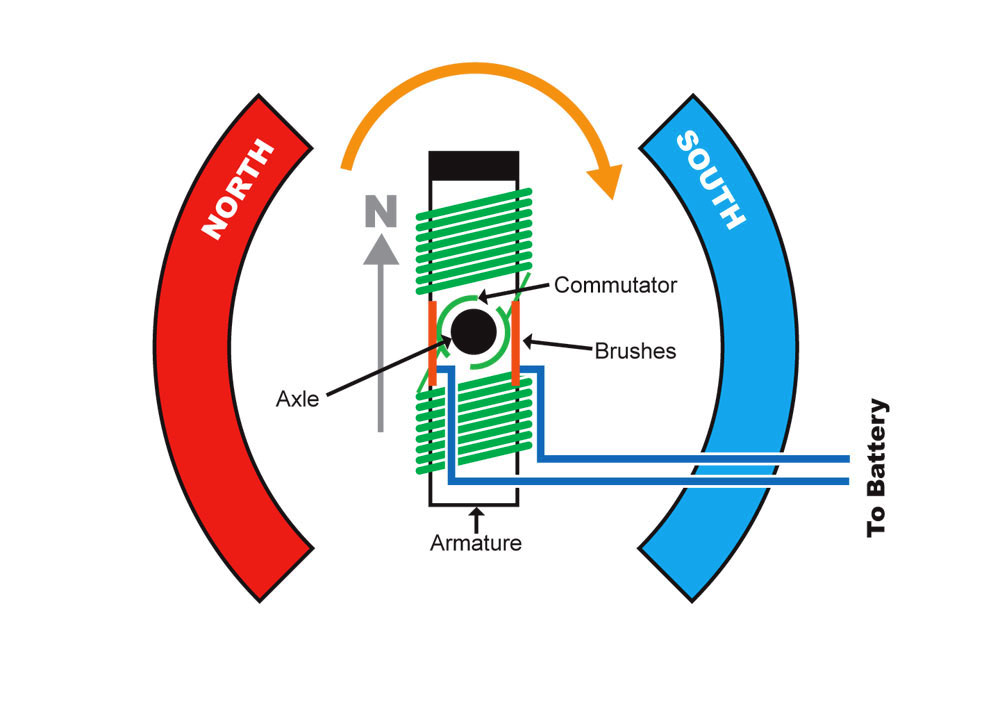
Key Specifications
Applications
Actuators
Electric, pneumatic, and hydraulic actuators for motion control
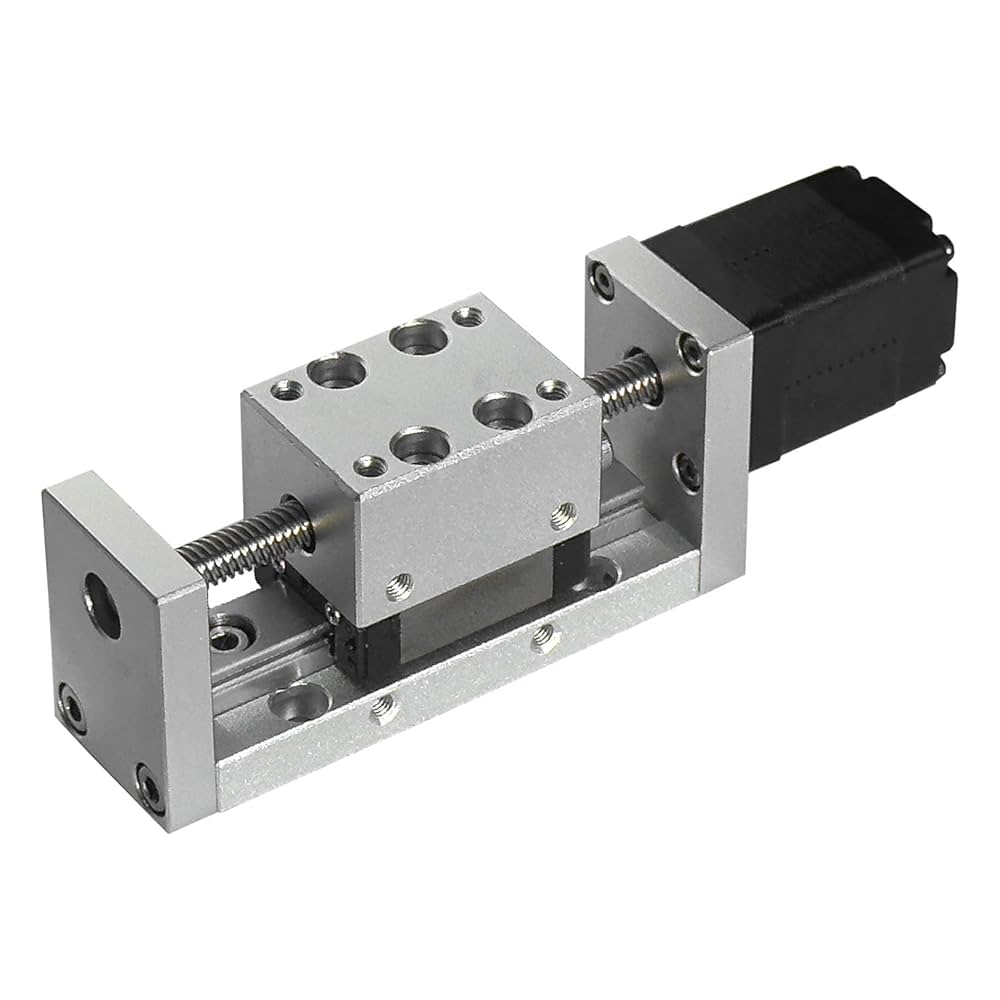

Key Specifications
Applications
O-Rings & Seals
Sealing solutions by material and form factor
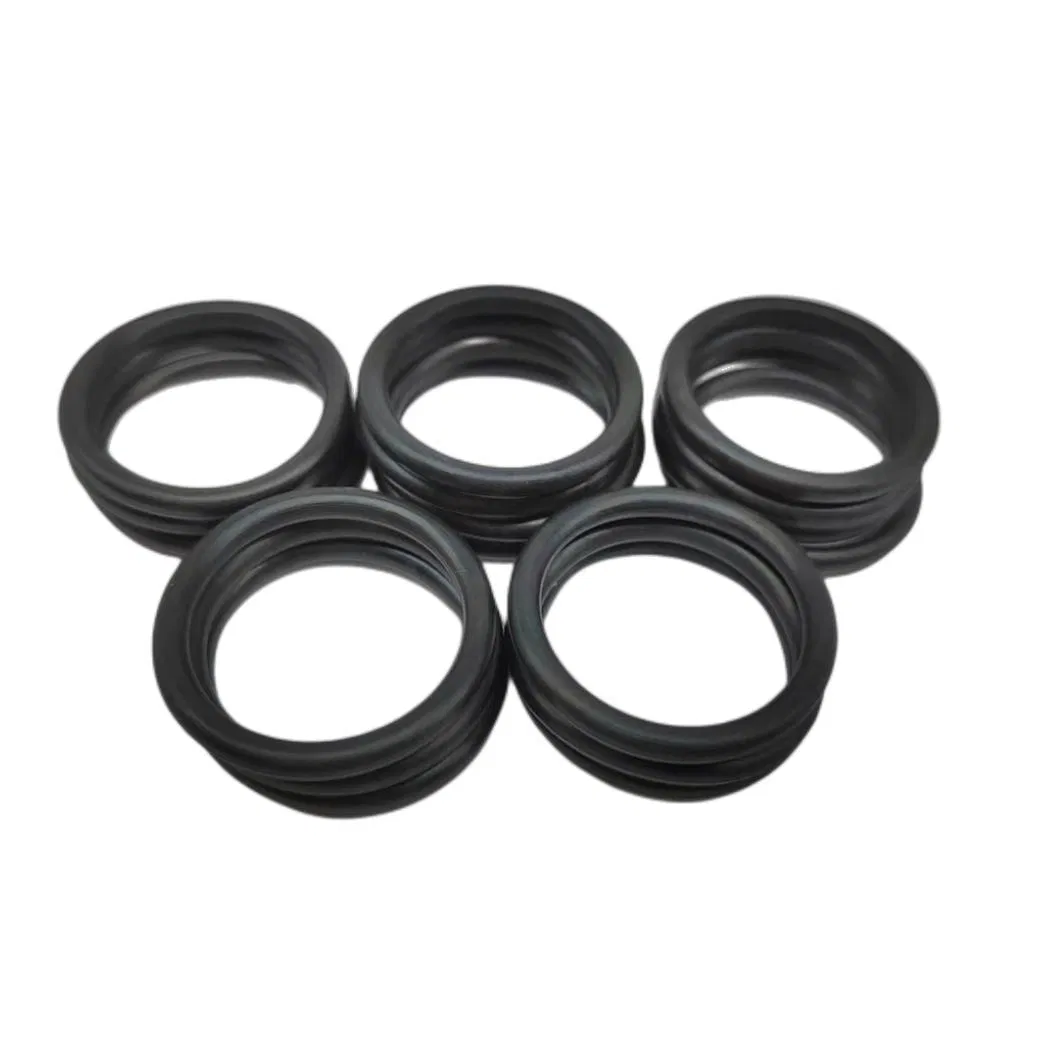

Key Specifications
Applications
Bearings
Ball, roller, thrust, and linear bearings for all load conditions

Key Specifications
Applications
Gears
Spur, helical, bevel, worm, planetary, and harmonic gears
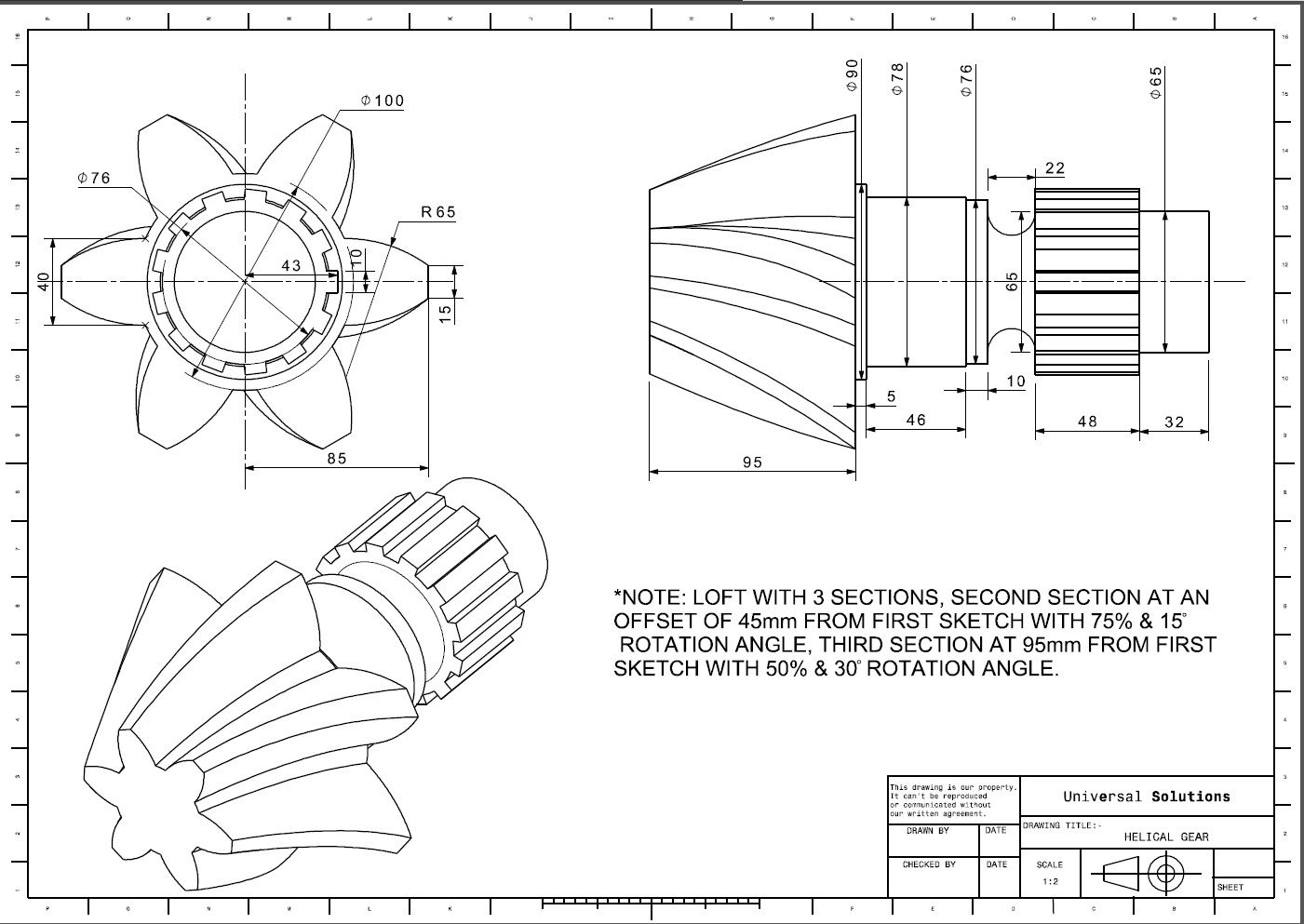
Key Specifications
Applications
Springs & Dampers
Helical, flat, disc springs and shock absorbers for energy storage and damping
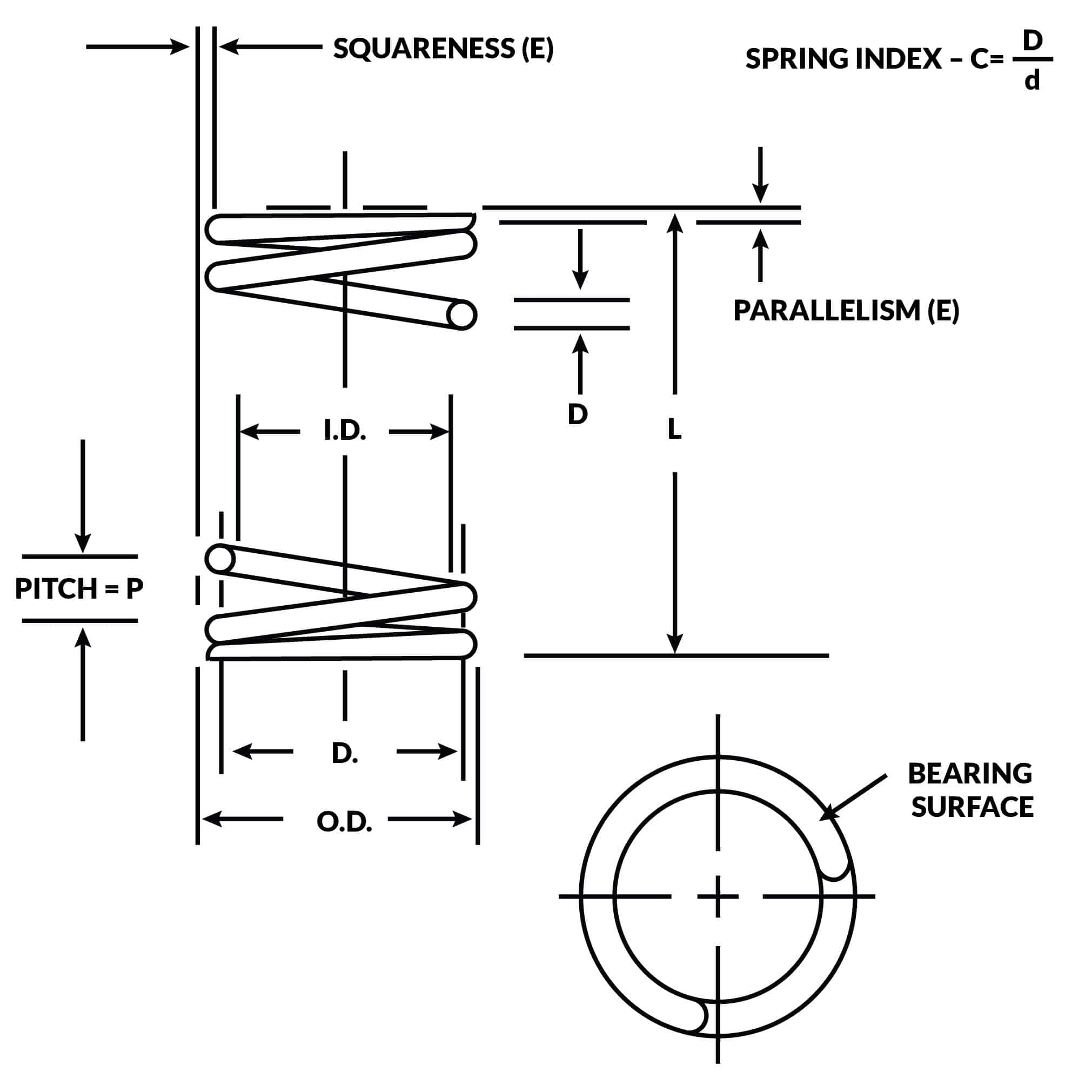
Key Specifications
Applications
Hardware & Fasteners
Comprehensive nuts, bolts, screws, and mechanical fastening systems
Key Specifications
Applications
Quick Selection Guide
Fast reference cards for component selection with key specifications, pros/cons, and when to use each type
Motors Quick Reference

DC Brushed Motor
Simple speed control needed
Key Specs
Advantages
Disadvantages
Applications
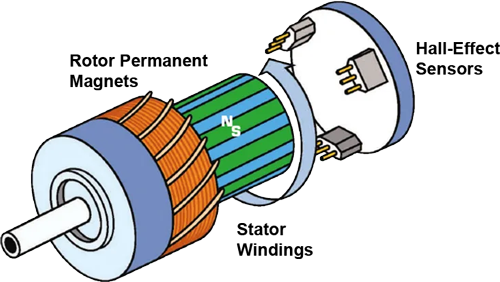
DC Brushless (BLDC)
High efficiency and long life needed
Key Specs
Advantages
Disadvantages
Applications
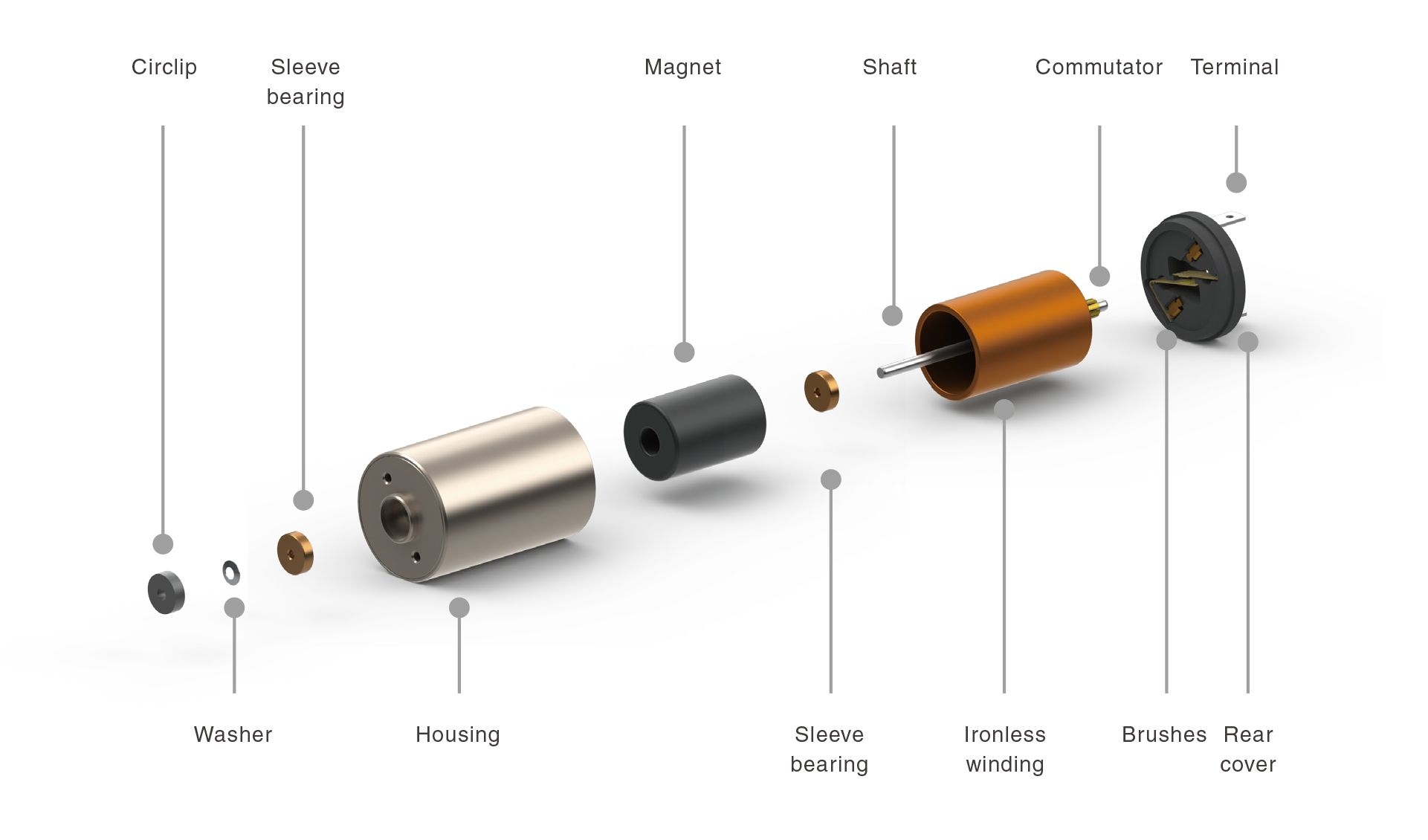
DC Coreless
Ultra-fast response required
Key Specs
Advantages
Disadvantages
Applications

AC Induction (Squirrel Cage)
Robust industrial applications
Key Specs
Advantages
Disadvantages
Applications
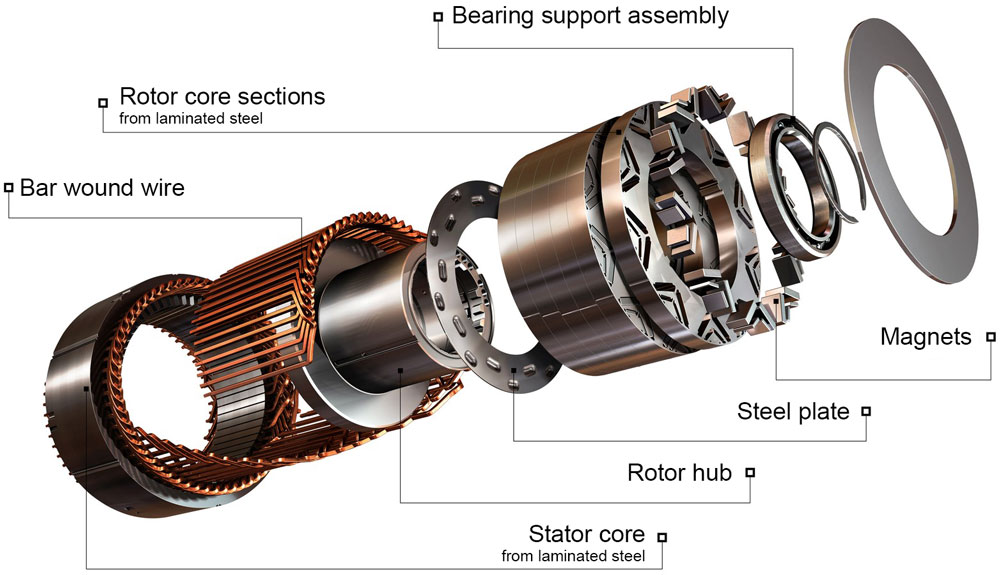
AC Synchronous (PMSM)
High efficiency and precise speed
Key Specs
Advantages
Disadvantages
Applications

Universal Motor
AC/DC operation needed
Key Specs
Advantages
Disadvantages
Applications
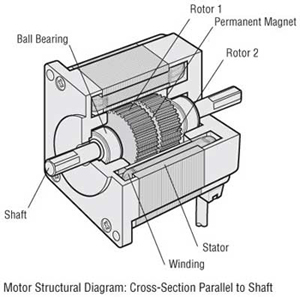
Stepper Motor
Open-loop positioning acceptable
Key Specs
Advantages
Disadvantages
Applications
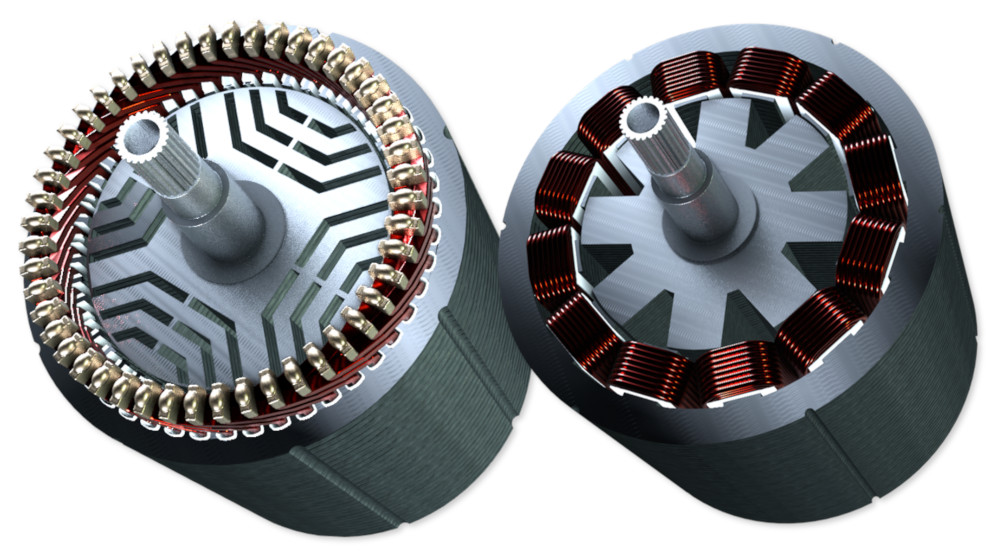
Switched Reluctance (SRM)
Harsh environments, fault tolerance
Key Specs
Advantages
Disadvantages
Applications

Linear Motor
Direct linear motion needed
Key Specs
Advantages
Disadvantages
Applications
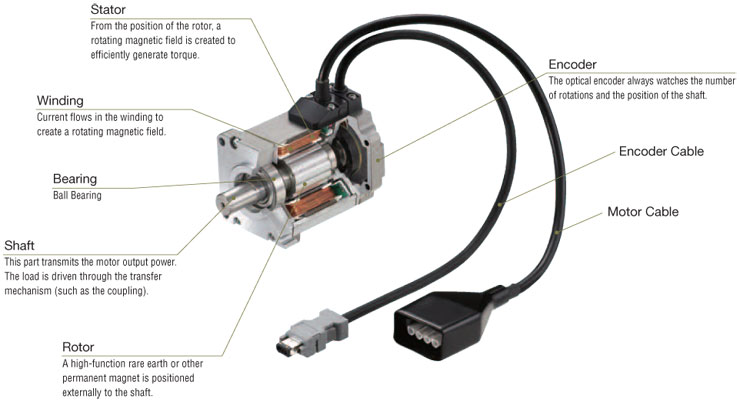
Servo Motor
High precision positioning required
Key Specs
Advantages
Disadvantages
Applications

Ultrasonic Motor
Silent, precise positioning
Key Specs
Advantages
Disadvantages
Applications
Component Comparison Tables
Side-by-side comparison of key specifications, performance characteristics, and selection criteria
Motor Comparison
Compare key characteristics to select the best option for your application
| Type | Efficiency | Speed Control | Cost | Maintenance | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DC Brushed | 75-80% | Simple | Low | High | Simple applications |
| DC Brushless | 85-90% | Complex | Medium | Low | High efficiency |
| AC Induction | 80-95% | Complex | Medium | Very Low | Industrial drives |
| Servo | 85-90% | Precise | High | Low | Precision control |
| Stepper | 70-85% | Digital | Medium | Very Low | Positioning |
Cost Considerations
Initial cost vs. operational cost over lifetime
Maintenance Requirements
Scheduled maintenance and service intervals
Environmental Factors
Operating conditions and environmental resistance
Manufacturing Processes Reference
Comprehensive guide to manufacturing processes with specifications, applications, and selection criteria
Surface Finishing
Detailed specifications and selection criteria for each manufacturing process

Anodizing
Electrochemical process for aluminum surface treatment
Compatible Materials
Key Specifications
Applications
Advantages
Considerations
Cost Factors
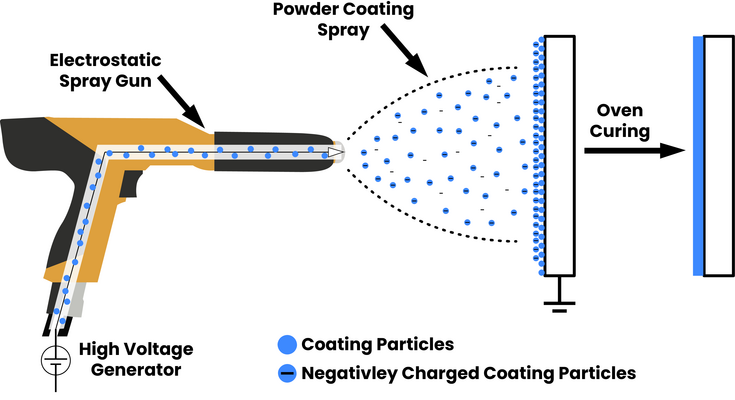
Powder Coating
Dry powder applied electrostatically and cured with heat
Compatible Materials
Key Specifications
Applications
Advantages
Considerations
Cost Factors
Lead Times
Process-dependent timing considerations
Cost Optimization
Volume and design considerations
Material Properties
Process-material compatibility
Quality Control
Inspection and testing requirements
Hardware & Fasteners Reference
Comprehensive catalog of nuts, bolts, and mechanical fastening systems for all applications
Nuts & Threading
Detailed specifications and selection criteria for each fastener type

General-Purpose Nuts
Standard nuts for general applications and structural use
Compatible Materials
Key Specifications
Applications
Advantages
Considerations
Cost Factors

Hand-Tightened Nuts
Nuts designed for hand assembly without tools
Compatible Materials
Key Specifications
Applications
Advantages
Considerations
Cost Factors

Locking Nuts (Vibration-Resistant)
Self-locking nuts that resist loosening from vibration
Compatible Materials
Key Specifications
Applications
Advantages
Considerations
Cost Factors

Flange & Integrated-Washer Nuts
Nuts with built-in washers or flanges for load distribution
Compatible Materials
Key Specifications
Applications
Advantages
Considerations
Cost Factors

Shaft, Bearing & Precision Nuts
Precision nuts for shafts, bearings, and tight-tolerance applications
Compatible Materials
Key Specifications
Applications
Advantages
Considerations
Cost Factors

Sheet-Metal, Captive & Blind Nuts
Nuts for thin materials and blind-side installation
Compatible Materials
Key Specifications
Applications
Advantages
Considerations
Cost Factors
Springs & Dampers Reference
Comprehensive guide to springs and shock absorbers for energy storage, force generation, and motion control
Springs
Detailed specifications and selection criteria for each component type

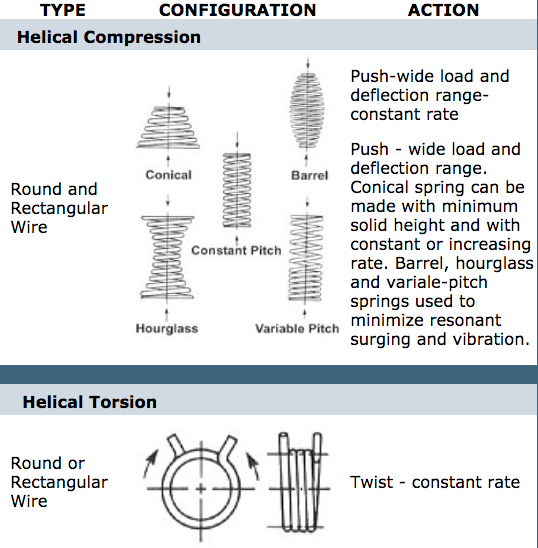
Helical Compression Springs
Round-wire coil springs that resist compression forces
Compatible Materials
Key Specifications
Applications
Advantages
Considerations
Cost Factors
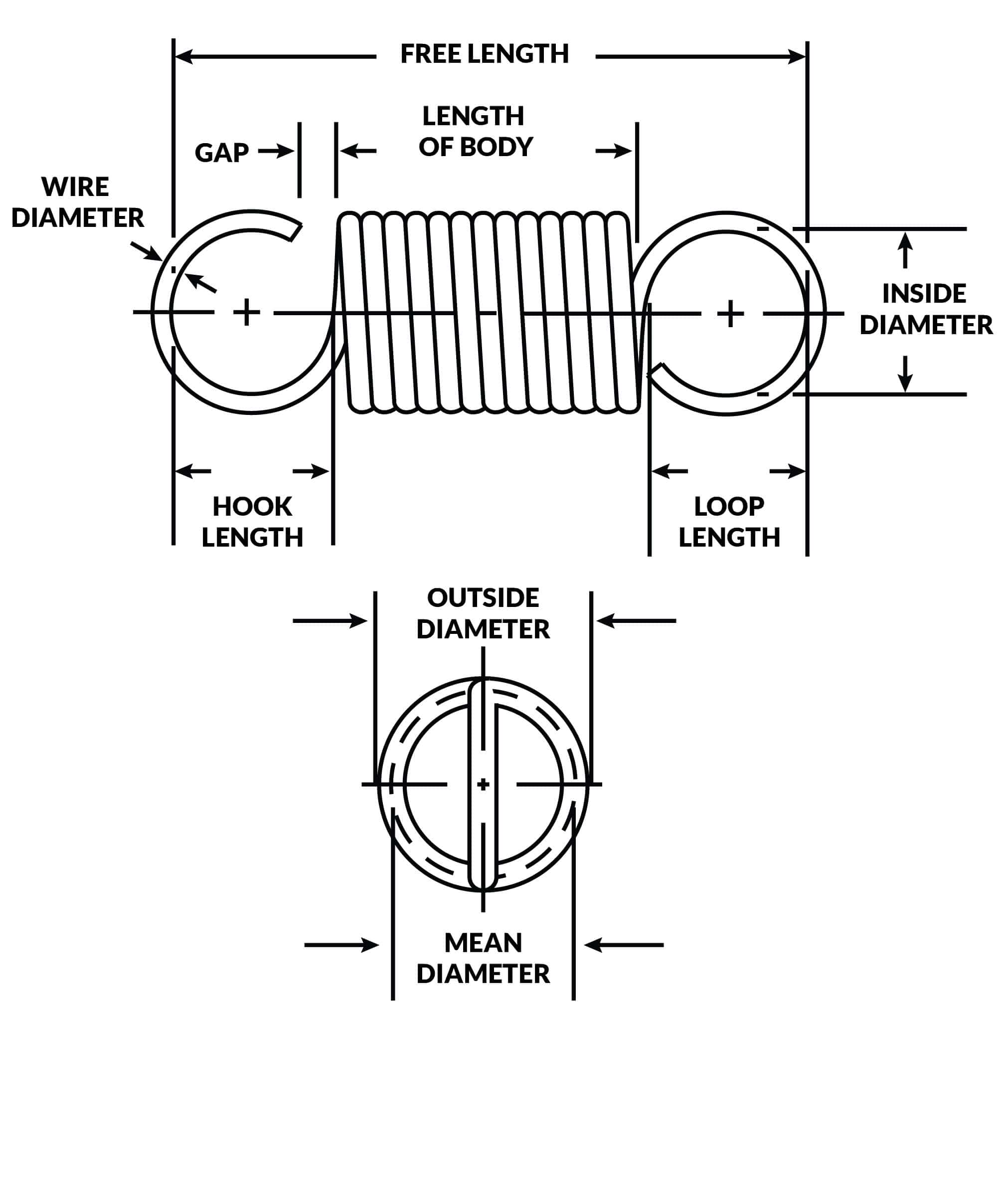
Helical Extension & Torsion Springs
Springs that resist tension forces or provide torque
Compatible Materials
Key Specifications
Applications
Advantages
Considerations
Cost Factors

Flat, Leaf & Spiral Springs
Flat strip springs for specialized applications
Compatible Materials
Key Specifications
Applications
Advantages
Considerations
Cost Factors
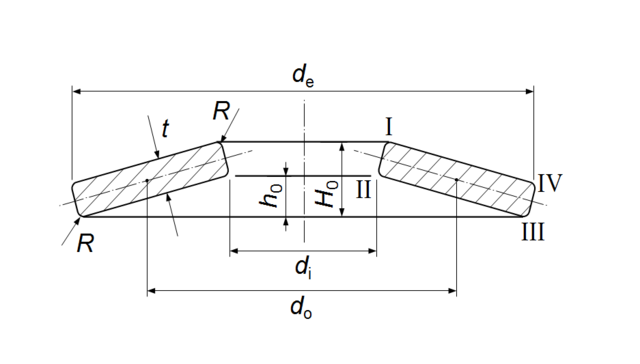
Disc & Washer Springs
Conical disc springs and wave washers for compact applications
Compatible Materials
Key Specifications
Applications
Advantages
Considerations
Cost Factors
Elastomeric & Air Springs
Rubber and air-based spring systems
Compatible Materials
Key Specifications
Applications
Advantages
Considerations
Cost Factors
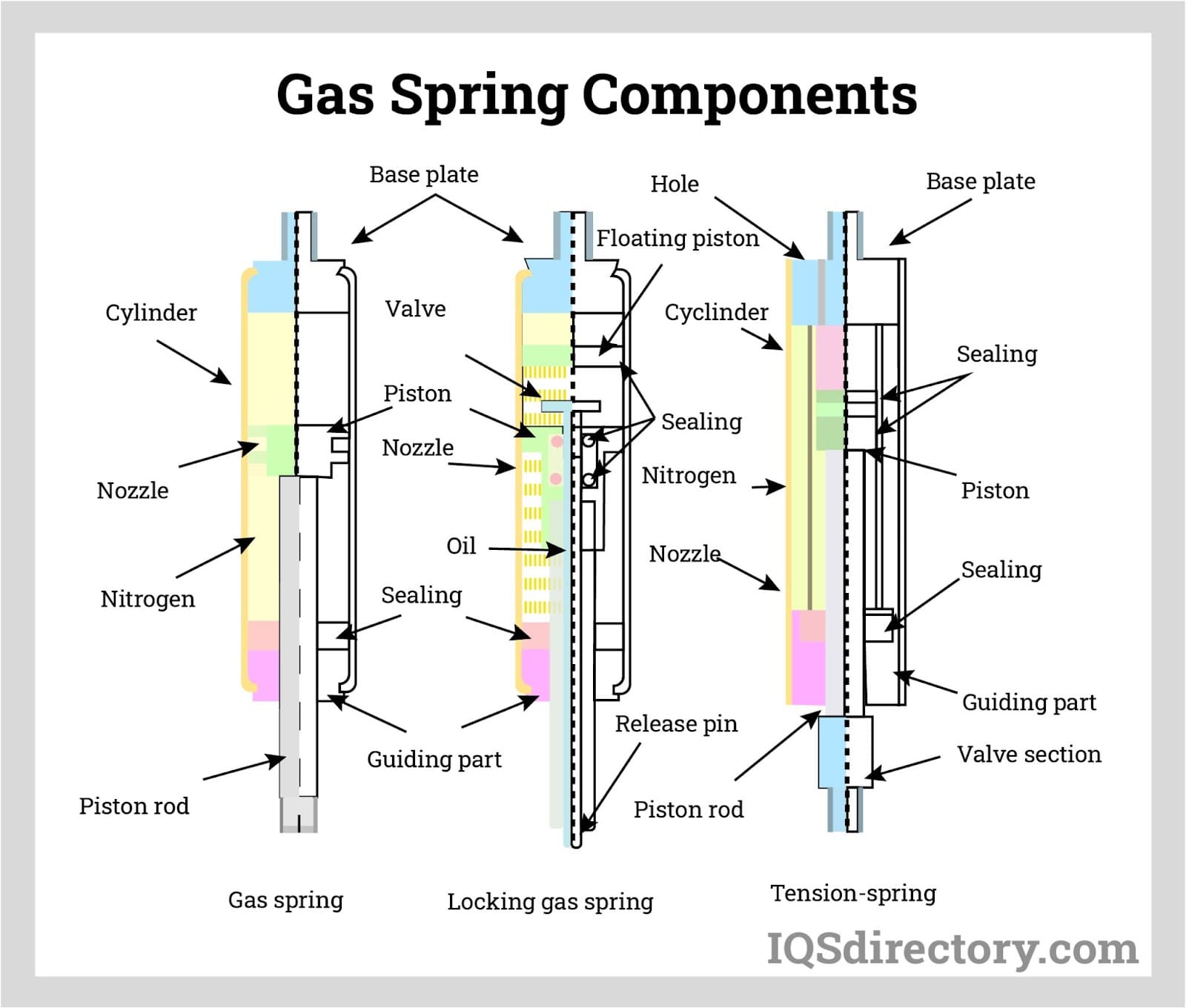
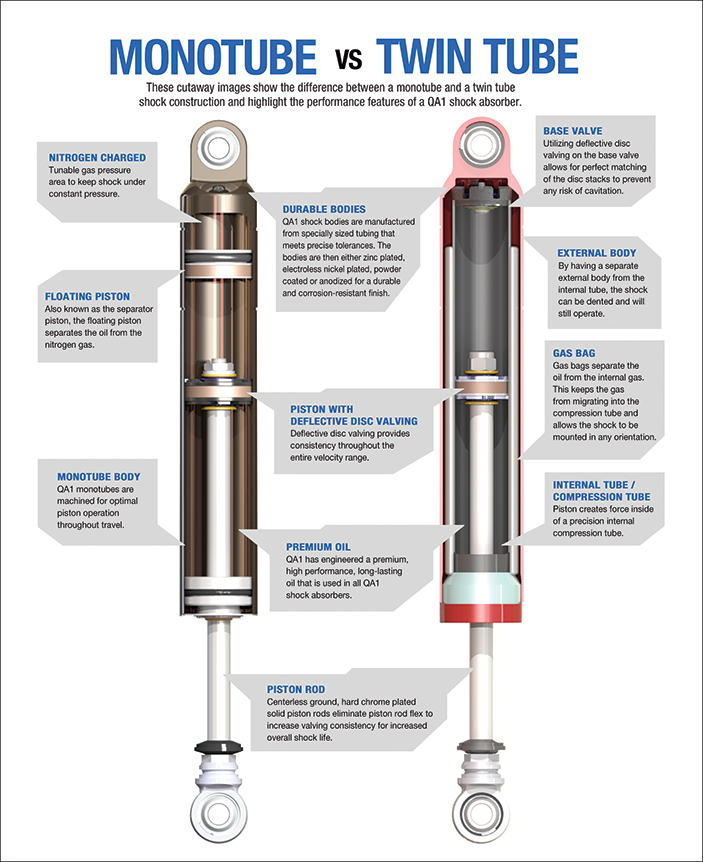
Gas & Hydraulic Springs
Pressurized gas and fluid-based spring systems
Compatible Materials
Key Specifications
Applications
Advantages
Considerations
Cost Factors
Specialty Springs & Retainers
Torsion bars and spring-action fasteners